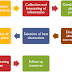
Basic Structure of C++
Basic Structure of C++
|
Documentation section
|
|||||
|
Link Section
|
|||||
|
Definition section
|
|||||
|
Global declaration Section
|
|||||
|
Class class_name
{
Class definition Section
};
return_type main(){ Main function section
statements;
}
|
1. Documentation Section:
This section contents set of comment line giving the name of the program, the author, algorithm, methods used and other details. This will be useful in future for the user and developing teams.
Eg. // This program is ….
2. Link Section
This section provides an instruction to the compiler to link classes, function, and operators with the program from the system library.
For eg:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
3. Definition section
In this section, all symbolic constants are defined.
For example: #define pi 3.14
4. Global declaration section
The variables which are used in more than one functions or blocks are called global variables.
5. Class definition section
This section contains all the user-defined class and their data members and function members.
6. Main Function section
Every C++ program starts main() function and it is called entry point function.
Within the main function, there are a declaration and executable parts.






No comments: